| [1] 陈恕柱,靳宏勇,刘毅东,等.舌黏膜与口腔黏膜在治疗多次尿道下裂手术失败患儿中的临床应用和比较[J].中华小儿外科杂志, 2017,38(1):59-63. [2] 任晓敏,蒋跃庆,姚海军,等.后型尿道下裂二期膀胱黏膜半管状重建尿道术的临床研究[J].现代泌尿外科杂志, 2011,16(6):502-504. [3] Weiser AC,Franco I,Herz DB,et al.Single layered small intestinal submucosa in the repair of severe chordee and complicated hypospadias.J Urol.2003;(4 Pt.2):1593-1595; disussion 1595-0.[4] 李振武,张潍平,孙宁,等.国内医院尿道下裂治疗现状调查[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2016,37(6):453-458. [5] 肖元宏,刘贵麟,刘洲禄.Onlay岛状皮瓣尿道成形术治疗儿童尿道下裂适应证及并发症防治[J].解放军医学院学报, 2016,37(11):1152-1154,1159.[6] 梁伟强,冀晨阳,张佳琦,等.尿道口周蒂肉膜瓣在阴茎中段型尿道下裂一期修复中的应用[J].中国美容整形外科杂志, 2017,28(2):107-111. [7] 江志勇,李学德,何庆鑫,等.组织覆盖技术在Snodgrass术治疗尿道下裂的应用研究进展[J].中国性科学,2016,25(1):24-27.[8] 唐耘熳.尿道下裂术后尿道狭窄、阴茎头裂开及尿道憩室的认识及处理[J].临床小儿外科杂志,2017,16(3):212-214. [9] 王德娟,李科,黄文涛,等.游离舌黏膜在儿童再次尿道下裂成形术中的应用[J].新医学,2016,47(4):242-245. [10] Sievert KD,Amend B,Stenzl A.Tissue engineering for the lower urinary tract: a review of a state of the art approach.Eur Urol. 2007;52(6): 1580-1589.[11] Atala A.Recent developments in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Curr Opin Pediatr.2006;18(2):167-171.[12] Svystonyuk DA,Mewhort HEM,Fedak PWM.Using Acellular Bioactive Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds to Enhance Endogenous Cardiac Repair. Front Cardiovasc Med.2018;5:35[13] Udelsman B,Mathisen DJ,Ott HC.Bioprosthetics and repair of complex aerodigestive defects.Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;7(2):284-292.[14] Emodi O,Ginini JG,van Aalst JA,et al.Cleft Palate Fistula Closure Utilizing Acellular Dermal Matrix.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open.2018; 6(3):e1682.[15] Griffith LG,Naughton G.Tissue engineering--current challenges and expanding opportunities. Science. 2002;295(5557):1009-1014. [16] Leslie B,Jesus LE,El-Hout Y,et al.Comparative histological and functional controlled analysis of tubularized incised plate urethroplasty with and without dorsal inlay graft: a preliminary experimental study in rabbits.J Urol.2011;186(4 Suppl):1631-1637.[17] Kanematsu A,Yamamoto S,Ogawa O.Changing concepts of bladder regeneration.Int J Urol. 2007;14(8):673-978.[18] Reyes M,Dudek A,Jahagirdar B,et al. Origin of endothelial progenitors in human postnatal bone marrow.J Clin Invest. 2002;109(3):337-346.[19] Nieda M,Nicol A,Denning-Kendall P,et al.Endothdial cell precursors are normal components of human umbilical cord blood.Br J Haematol. 1997;98(3):775-777.[20] Tamaki T,Akatsuka A,Ando K,et al.Identification of myogenic- endothelial progenitor cells in the interstitial spaces of skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol.2002;157(4):571-577.[21] Dahms SE,Piechota HJ,Dahiya R,et al.Composition and biomechanical properties of the bladder acellular matrix graft: comparative analysis in rat, pig and human.Br J Urol. 1998;82(3):411-419.[22] De Filippo RE,Yoo JJ,Atala A.Urethral replacement using cell seeded tubularized collagen matrices.J Urol.2002;168(4-2):1789-1792.[23] Shokeir A,Osman Y,El-Sherbiny M,et al.Comparison of Partial Urethral Replacement with Acellular Matrix versus Spontaneous Urethral Regeneration in a Canine Model.Eur Urol. 2003;44(5): 603-609. [24] Atala A,Guzman L,Retik AB.A novel inert collagen matrix for hypospadias repair.J Urol. 1999;162(3 Pt 2):1148-1151.[25] Kanematsu A,Yamamoto S,Noguchi T,et al.Bladder regeneration by bladder acellular matrix combined with sustained release of exogenous growth factor.J Urol. 2003;170(4 Pt 2):1633-1638.[26] Kanematsu A,Yamamoto S,Ozeki M,et al.Collagenous matrices as release carriers of exogenous growth factors. Biomaterials. 2004; 25(18):4513-4520.[27] Youssif M,Shiina H,Urakami S,et al.Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor Oil regeneration of blader acellular matrix graft:histologic and functional evaluation.Urology. 2005;66(1):201-207.[28] Wang JH,Xu YM,Fu Q,et al.Continued sustained release of VEGF by PLGA nanospheres modified BAMG stent for the anterior urethral reconstruction of rabbit.Asian Pac J Trop Med.2013;6(6):481-484.[29] Xiong Q,Lin H,Hua X,et al.A nanomedicine approach to effectively inhibit contracture during bladder acellularmatrix allograft-induced bladder regeneration by sustained delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor.Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(1-2):45-52.[30] Jiang X,Xiong Q,Xu G,et al.VEGF-Loaded Nanoparticle-Modified BAMAs Enhance Angiogenesis and Inhibit Graft Shrinkage in Tissue-Engineered Bladder.Ann Biomed Eng.2015;43(10):2577-2586.[31] Roelofs LA,Oosterwijk E,Kortmann BB,et al.Bladder Regeneration Using a Smart Acellular Collagen Scaffold with Growth Factors VEGF, FGF2 and HB-EGF.Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(1-2):83-92. [32] Wang L,Shi Q,Dai J,et al.vascularization promotes functional recovery in the transected spinal cord rats by implanted vascular endothelial growth factor-targeting collagenscaffold.J Orthop Res. 2018;36(3):1024-1034.[33] Ferrara N,Henzel WJ.Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2012;425(3):540-547.[34] Koch S,Yao CH,Grieb G,et al.Enhancing angiogenesis in collagen matrices by covalent incorporation of VEGF.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17(8):735-741.[35] Yao N,Gao M,Ren K,et al.PD806: a novel oral vascular disrupting agent shows antitumor and antivascular effects in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Drugs.2015;26(2):148-159.[36] Giatromanolaki A,Koukourakis MI,Theodossiou D,et al. Comparative evaluation of angiogenesis assessment with anti-factor-VIII and anti-CD31 immunostaining in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.1997;3(12 Pt 1):2485-2492. |
.jpg)
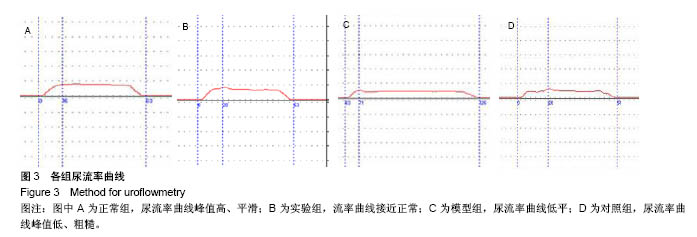

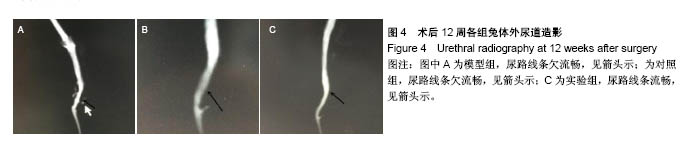
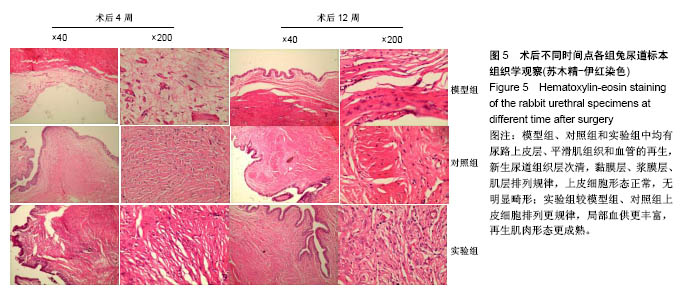
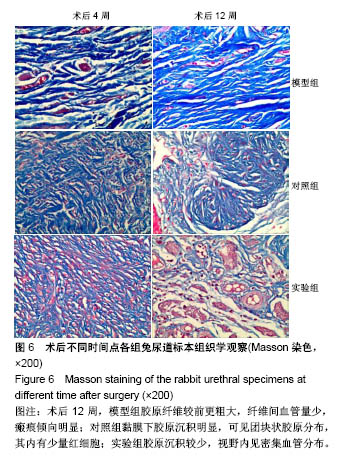
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)